Due to massive growth and an increase in the computing power of the IoT (Internet of Things) devices, there has been an exceptional volume of data. For instance, as the 5G networks get more common and continue to increase, so will the data volumes. Previously, AI and the cloud claimed to automate and also speed innovation, and it planned on doing that by driving the actionable insights from data. However, the complexity of data that gets created through connected devices has outpaced the infrastructure and the network capabilities. Moreover, transferring all of that device-generated data onto a centralized data center causes issues with the latency and bandwidth. That is where edge computing comes in.
Edge computing offers a better alternative where the data gets processed and then evaluated close to the point from where it was created. Since the data doesn’t cross over a network and into a data center or a cloud in order to be processed, this results in the latency being reduced significantly. Edge computing allows a more detailed and faster data analysis, which results in quicker response times, deeper insights, and greatly-improved customer experiences.
What Is Meant By Edge Computing?
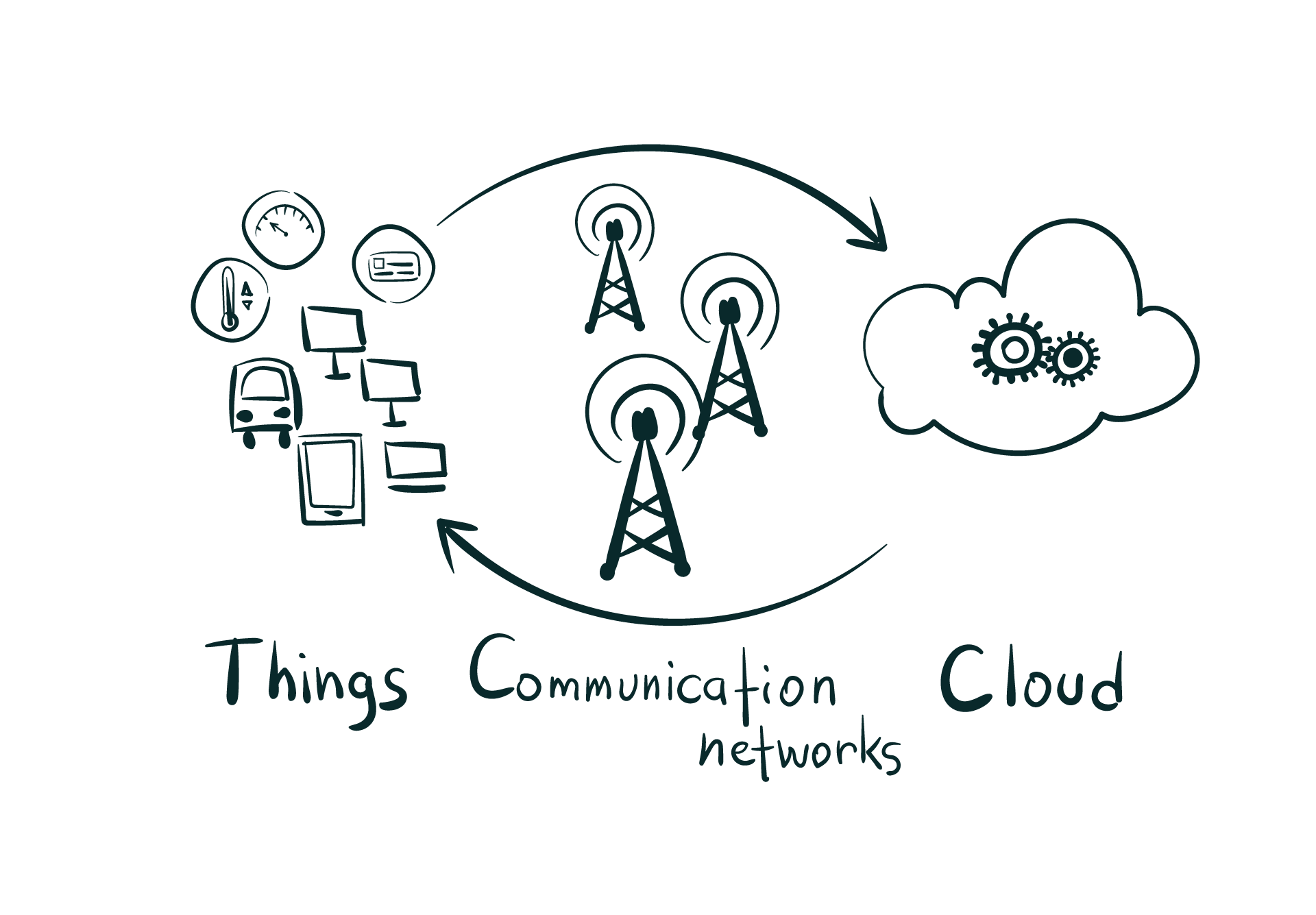
Edge computing is known as a distributed and open IT architecture, which contains decentralized processing power that enables mobile computing and IoT technologies. When it comes to edge computing, instead of being transmitted into a data center, the device itself processes the data or it is processed by a local server or computer.
Moreover, edge computing allows data stream acceleration, which includes data processing in real-time without any latency. Through this, smart devices and applications end up responding to data pretty much straight away and while it is being created, which eliminates any lag time. This is highly important for different technologies like self-driving cars and also comes with several benefits for a business.
With edge computing, you get efficient data processing, meaning massive quantity of data is able to be processed close to the course, which reduces internet bandwidth usage. This ends up eliminating costs and making sure that applications can be effectively used in remote areas. Also, using this way to process data ensures that you don’t have to worry about sharing this data in a public cloud; hence, adding a security layer for any sensitive
What Is Edge Computing Used For?
Edge computing is also known as a distributed computing framework, which carries enterprise applications closer to the data sources like local edge servers. This closeness to the data at its source offers strong business benefits, quicker insights, better bandwidth availability, and improved response times.
Edge computing can be used for and be a part of numerous products, applications, and services. Some of those are listed here:
For monitoring security systems.
All IoT devices, meaning smart devices that can connect to the internet. These devices can greatly benefit from running the code on the device instead of the cloud, which will result in highly-efficient user interactions.
Self-driving cars can benefit from edge computing as well since autonomous vehicles are reacting in real-time and don’t wait for the instructions from a server.
There is more efficient caching. When a code is run on the CDN edge network, then an application is able to customize how the content is cached so that it can efficiently serve the content to the users.
Medical monitoring devices can benefit from edge computing as well. It is important that medical devices are able to respond in real-time and do not have to wait for commands from a cloud server.
Interactive live video, such as video conferencing, ends up using a lot of bandwidth; hence, moving the backend processes near the source of the video will result in decreasing the latency and the lag.
Example Of Edge Computing
Here is an example of edge computing in order to further understand it. A building consists of several high-definition IoT video cameras. All of these cameras are ‘dumb’ cameras, meaning they simply send a raw video signal and stream that signal continuously to a cloud server. On this cloud server, all of the cameras’ video output gets put through the motion-detection application in order to make sure that only video footage that features any activity is being saved to the database of the server. Hence, there will always be a constant strain on the internet infrastructure of that building, since a lot of bandwidth is being consumed in a high volume of the video footage that’s being transferred. In addition to all this, there is also quite a bit of a heavy load on this cloud server, which is responsible for simultaneously processing the video clips from all of the cameras.
Now let’s think about what will happen when the motion sensor computation gets transferred to the network edge. Every camera will be able to use its internal computer in order to work the motion-detecting application, which also includes sending the footage onto the cloud server as required. This will significantly reduce the bandwidth use since the majority of the camera footage isn’t going to travel into the cloud server.
Therefore, the cloud server’s only responsibility would be to store just the important footage. This means that the server is going to communicate with numerous cameras and not get overloaded. That is what edge computing really looks like.


What Are The Benefits Of Edge Computing?
1. Savings Of Costs
Edge computing helps in minimizing bandwidth use plus server resources. Both cloud resources and bandwidth are limited and also cost a lot of money. Nowadays, homes and offices are installing the latest smart thermostats, printers, cameras, and other applications. According to Statista, by the year 2025, there are going to be more than 75 billion IoT devices that will be installed all over the world. To support these devices, all of the important computation will need to be transferred to the edge.


2. Improved Performance
Another great benefit of switching processes to edge computing is for reducing latency. Whenever there is the need for a device to communicate with a server somewhere distant, this will create a delay. An example of that would be when two colleagues are communicating over an instant messaging platform in the same office and experiencing a delay since every message requires being routed out of the office building, connect with any server somewhere around the world, and then brought back before the message appears on the screen of the recipient. On the other hand, when that process is switched to edge computing, and the internal router of the company is responsible for transferring the intra-office chats, then that delay will not be there anymore.
Likewise, when users of different web applications have to face the processes that connect with an external server, they’re going to come across delays. The length of these delays will depend on the server’s location and the available bandwidth. However, all of these delays can easily be avoided when more processes are brought to the network edge.
3. New And Enhanced Functionality
Edge computing can also offer new functionality, which wasn’t available previously. An example of that would be a company that uses edge computing in order to process and evaluate their data by the edge, making it possible to do it in real-time.

4. Better Speed
Speed is an important aspect of a lot of businesses. For example, the financial sector of a company depends on the high-frequency trading algorithms, which means that a delay of even a few milliseconds could end up costing them a lot. Like, within the healthcare industry, this loss of time could actually impact someone’s life or death. Plus, for other businesses that offer data-driven services to their customers, delayed speed will end up frustrating the customers, causing long-term damage to the brand.
Therefore, one of the greatest things about edge computing is how it can improve network performance just by reducing the latency. Generally, the IoT edge computing devices tend to process data locally or within the edge data centers that are nearby. Hence, the information that they gather does not require traveling as far as it usually would under the standard cloud architecture.
Thus, edge computing can reduce latency in a great manner by processing the data that’s closer to the source and cutting the physical distance that it needs to travel. This results in better speed for the users, where latency is measure in microseconds instead of milliseconds. Knowing that even a slight moment of latency could result in costing companies hundreds of dollars, the enhanced speed advantages that come with edge computing cannot go unnoticed.
5. Advance Security
There are also some crucial security advantages that come with edge computing. When it comes to the standard cloud computing architecture, it is inherently centralized, making it extremely vulnerable to DDoS (distributed denial of service) attacks plus power outages. On the other hand, edge computing actually distributes the storage, processing, and applications all across a range of data centers and devices, making it hard for even a single disruption to dismantle the network.
There is a major concern regarding IoT edge computing devices that they can be used as entry points for cyberattacks and allow malware or any other invasions to impact a network from any single weak point. Even though this is a real risk, an edge-computing architecture’s distributed nature makes it a lot easier to apply security protocols, which end up sealing any compromised portions that do not require shutting down the whole network.
Moreover, there is a lot of data that is being processed on the local devices instead of transmitting it back onto a central data center; hence, edge computing ends up reducing the amount of data that are actually at risk. Also, there is fewer data available that’s intercepted during the transfer; hence, even if any device gets compromised, there will only be the data that has been collected locally instead of the large amount of data that could potentially be exposed through a compromised server.
The edge computing architecture includes specialized edge data centers, and because of this, there are extra security measures available in order to protect against DDoS attacks and any other cyberattacks. The ideal edge data center contains numerous tools that the clients can utilize in order to monitor and also secure their networks.

What Is IoT Edge Computing?
IoT (Internet of Things) has become quite important in both the consumer and also the industrial markets. Since high bandwidth internet connections have become available, especially with the rise of the 5G networks, this has given a rise to innovative IoT solutions in different areas, like automotive, smart cities, healthcare, energy, supply chain, and so on. Whether it is enterprises, businesses, or even inside people’s homes, everyone is always surrounded by connected devices.
Even though a lot of today’s tech devices are taking advantage of cloud computing, IoT manufacturers, including the application developers, have begun to see the benefits of performing more compute plus analytics on the devices. Hence, this new approach results in reducing latency for the critical applications, not depending as much on the cloud, and better maintenance of the large amount of data that’s being created by the IoT. A great example of that is the latest indoor security cameras that use on-device vision processing in order to look out for any motion, tell apart the different family members, and only send alerts when the cameras come across someone they don’t recognize. Due to this, there is a reduction in the bandwidth cloud’s processing amount, including the cloud storage used as compared to sending video footage over the network. Also, due to on-device processing, the speed of alerts gets improved as well as it reduces the chances of any false alarms.
Edge computing is the ability to do on-device processing plus analytics, where ‘edge’ is the world of devices and gateways connected through the internet that’s sitting on the field, which is the equivalent to the ‘cloud.’
Due to edge computing, there are countless new possibilities that can be seen within IoT applications. This is particularly great for applications that depend on machine learning for different tasks, like face recognition, object detection, avoiding obstacles, and language processing.
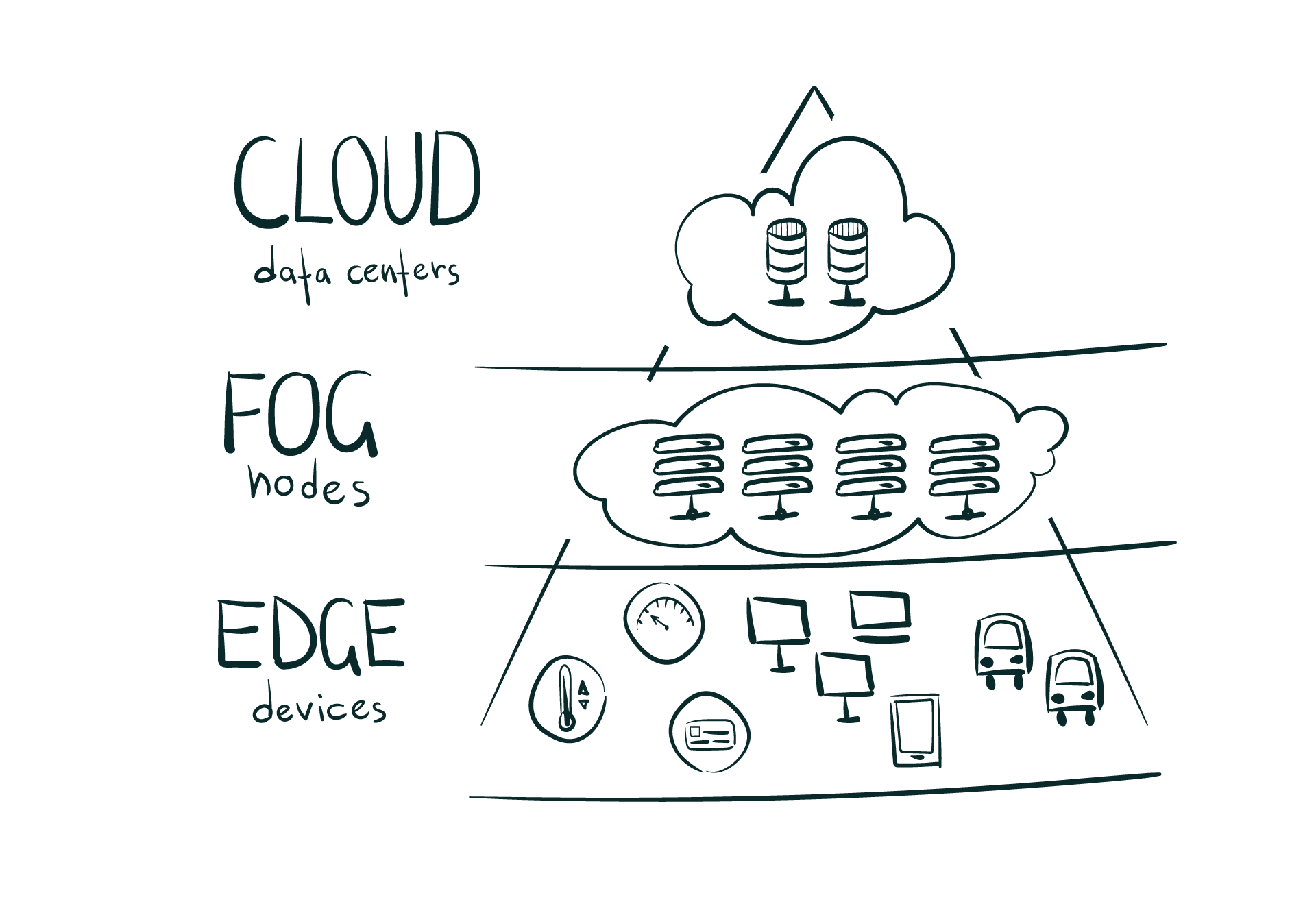
Fog Computing VS Edge Computing
In today’s world, IoT devices are quickly spreading all over the globe. According to studies, by 2025 there will be over 75 billion active IoT devices available all over the world, as mentioned previously. Whether it is in-store beacons or smart voice assistants, different brands are experimenting with this in order to improve the experiences of their customers and at the same time gather data in a fresh and inventive way. The only issue is the large amount of data that is being accumulated from each device. So, how can one process this large amount of data?
That is where fog computing and edge computing come into the picture as two potential solutions. Both of these computing solutions offer the same functionalities when it comes to pushing both intelligence and data towards analytic platforms, which are situated nearby where the data was originated from, whether that is through speakers, screens, pumps, motors, or sensors.
Both fog computing plus edge computing are quite similar to each other. They are both responsible for influencing the computing capabilities inside a local network in order to perform computation tasks that are usually performed in the cloud.

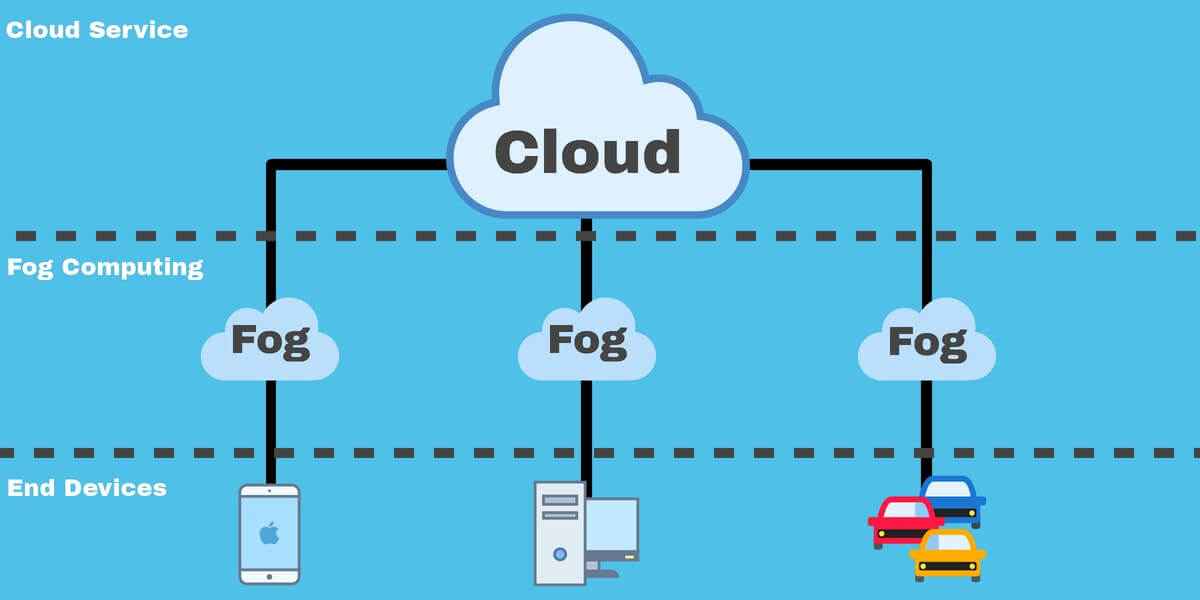
Furthermore, both of these technologies can assist organizations in reducing their dependence on cloud-based platforms in order to analyze data that oftentimes leads to certain latency issues. These technologies can help in making data-driven decisions a lot faster.
On the other hand, when it comes to the main difference between the two, both of these technologies process data in different areas. Usually, edge computing occurs on the devices directly, on which the sensors are connected, or a gateway device that’s physically near the sensors. When it comes to fog computing, it usually transfers the edge computing activities onto the processors which are connected to LAN or within the LAN hardware, so that they are physically a bit far away from the sensors and the actuators.
Hence, in fog computing, the data that gets processed is within a fog node or the IoT gateway that can be found within the LAN. In the case of edge computing, the data gets processed on the device itself or the sensor without going anywhere else.
Conclusion
In the end, it is quite clear that even though the initial aim of edge computing was reducing bandwidth costs for the IoT devices over several long distances, it is the development of the real-time applications, which need local processing plus storage capabilities, that is going to further move the technology forward as time goes on. Edge computing has truly changed the way the world works when it comes to technology and it is not going to stop anytime soon. It will only get better from here as technology gets more advanced.
Learn More

Contact RankWorks™ today to learn how Edge Computing can help your business grow, connect and convert more online.

